Data warehouse architecture defines the comprehensive architecture of data processing and presentation that will be useful for data analysis and decision making within the enterprise and organization. Each organization has different data warehouses depending upon their need, but all of them are characterized by some standard components.
Data Warehouse applications are designed to support the user’s data requirements, an example of this is online analytical processing (OLAP). These include functions such as forecasting, profiling, summary reporting, and trend analysis.
The architecture of the data warehouse mainly consists of the proper arrangement of its elements, to build an efficient data warehouse with software and hardware components. The elements and components may vary based on the requirement of organizations. All of these depend on the organization’s circumstances.
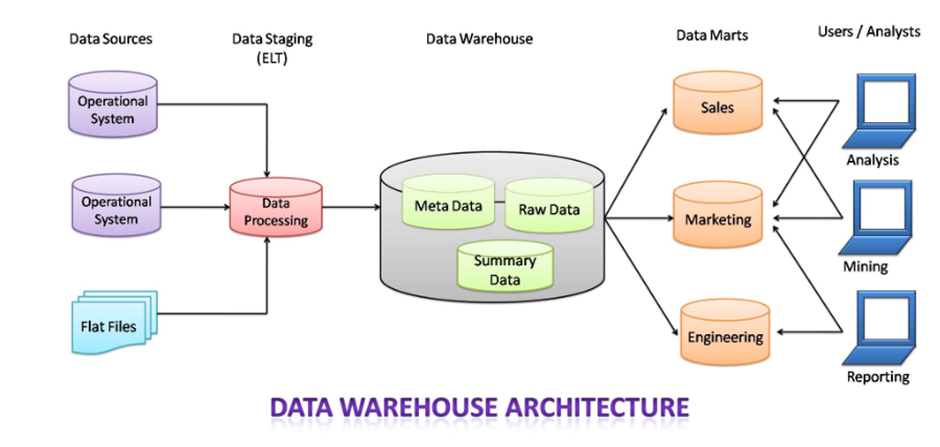
1. Source Data Component:
In the Data Warehouse, the source data comes from different places. They are group into four categories:
- External Data: For data gathering, most of the executives and data analysts rely on information coming from external sources for a numerous amount of the information they use. They use statistical features associated with their organization that is brought out by some external sources and department.
- Internal Data: In every organization, the consumer keeps their “private” spreadsheets, reports, client profiles, and generally even department databases. This is often the interior information, a part that might be helpful in every data warehouse.
- Operational System data: Operational systems are principally meant to run the business. In each operation system, we periodically take the old data and store it in achieved files.
- Flat files: A flat file is nothing but a text database that stores data in a plain text format. Flat files generally are text files that have all data processing and structure markup removed. A flat file contains a table with a single record per line.
2. Data Staging:
After the data is extracted from various sources, now it’s time to prepare the data files for storing in the data warehouse. The extracted data collected from various sources must be transformed and made ready in a format that is suitable to be saved in the data warehouse for querying and analysis. The data staging contains three primary functions
that take place in this part:
- Data Extraction: This stage handles various data sources. Data analysts should employ suitable techniques for every data source.
- Data Transformation: As we all know, information for a knowledge warehouse comes from many alternative sources. If information extraction for a data warehouse posture huge challenges, information transformation gifts even important challenges. We tend to perform many individual tasks as a part of information transformation. First, we tend to clean the info extracted from every source of data. Standardization of information elements forms an outsized part of data transformation. Data transformation contains several kinds of combining items of information from totally different sources. Information transformation additionally contains purging supply information that’s not helpful and separating outsourced records into new mixtures. Once the data transformation performs ends, we’ve got a set of integrated information that’s clean, standardized, and summarized.
- Data Loading: When we complete the structure and construction of the data warehouse and go live for the first time, we do the initial loading of the data into the data warehouse storage. The initial load moves high volumes of data consuming a considerable amount of time.
3. Data Storage in Warehouse:
Data storage for data warehousing is split into multiple repositories. These data repositories contain structured data in a very highly
normalized form for fast and efficient processing.
- Metadata: Metadata means data about data i.e. it summarizes basic details regarding data, creating findings & operating with explicit instances of data. Metadata is generated by an additional correction or automatically and can contain basic information about data.
- Raw Data: Raw data is a set of data and information that has not yet been processed and was delivered from a particular data entity to the data supplier and hasn’t been processed nonetheless by machine or human. This data is gathered out from online sources to deliver deep insight into users’ online behavior.
- Summary Data or Data summary: Data summary is an easy term for a brief conclusion of an enormous theory or a paragraph. This is often one thing where analysts write the code and in the end, they declare the ultimate end in the form of summarizing data. Data summary is the most essential thing in data mining and processing.
4. Data Marts:
Data marts are also the part of storage component in a data warehouse. It can store the information of a specific function of an organization that is handled by a
single authority. There may be any number of data marts in a particular organization depending upon the functions. In short, data marts contain subsets of the data stored in data warehouses.
Now, the users and analysts can use data for various applications like reporting, analyzing, mining, etc. The data is made available to them whenever required.
Data Warehousing life Cycle:
As we know the data warehouse is made by combining data from multiple diverse sources and the tools that support analytical reporting, structured and unstructured queries, and decision making for the organization. We need to follow the step by step approach for building and successfully implementing the Data Warehouse:
How does Data Warehouse work?
A Data Warehouse is like a central depository where data comes from different data sources. In a data warehouse, the data flows from the transactional system and relational databases. A data warehouse timely pulls out the data from various apps and systems, after then, the data goes through various processing and formatting and makes the data in a format that matches the data already in the warehouse. This processed data is stored in the data warehouses that ready for further analysis for decision making. The data formatting and processing depends upon the need of the organization
The Data could be in one of the following formats:
- Structured
- Semi-structured
- Unstructured data
The data is processed and transformed so that users and analysts can access the processed data in the Data Warehouse through Business Intelligence tools, SQL clients, and spreadsheets. A data warehouse merges all information coming from various sources into one global and complete database. By merging all of this information in one place, it becomes easier for an organization to analyze its customers more comprehensively.